Overview
We understand that navigating the complexities of overtime pay can be challenging. The tax rate for overtime pay mirrors that of regular wages. However, additional earnings from overtime can elevate an employee into a higher tax bracket, potentially impacting overall tax obligations. It's common to feel overwhelmed by these changes.
Fortunately, recent legislative adjustments offer some relief. Qualifying workers can now deduct a portion of their extra earnings from taxable income. This deduction could ease the financial burden that often accompanies increased earnings from overtime, providing a bit of breathing room.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you understand your options and make the most of your earnings. If you have further questions or need assistance, please reach out.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of overtime pay is essential for employees like you who want to maximize earnings and navigate the complexities of tax implications. We recognize that with the upcoming changes to salary thresholds and new legislative provisions, the landscape of overtime compensation is evolving. This presents both opportunities and challenges.
How can you effectively manage your expectations regarding the tax rate for overtime pay while ensuring you benefit from your additional hours? In this article, we delve into the critical aspects of overtime pay, debunking common myths and exploring the latest changes that could significantly impact your take-home income.
You're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you make sense of it all.
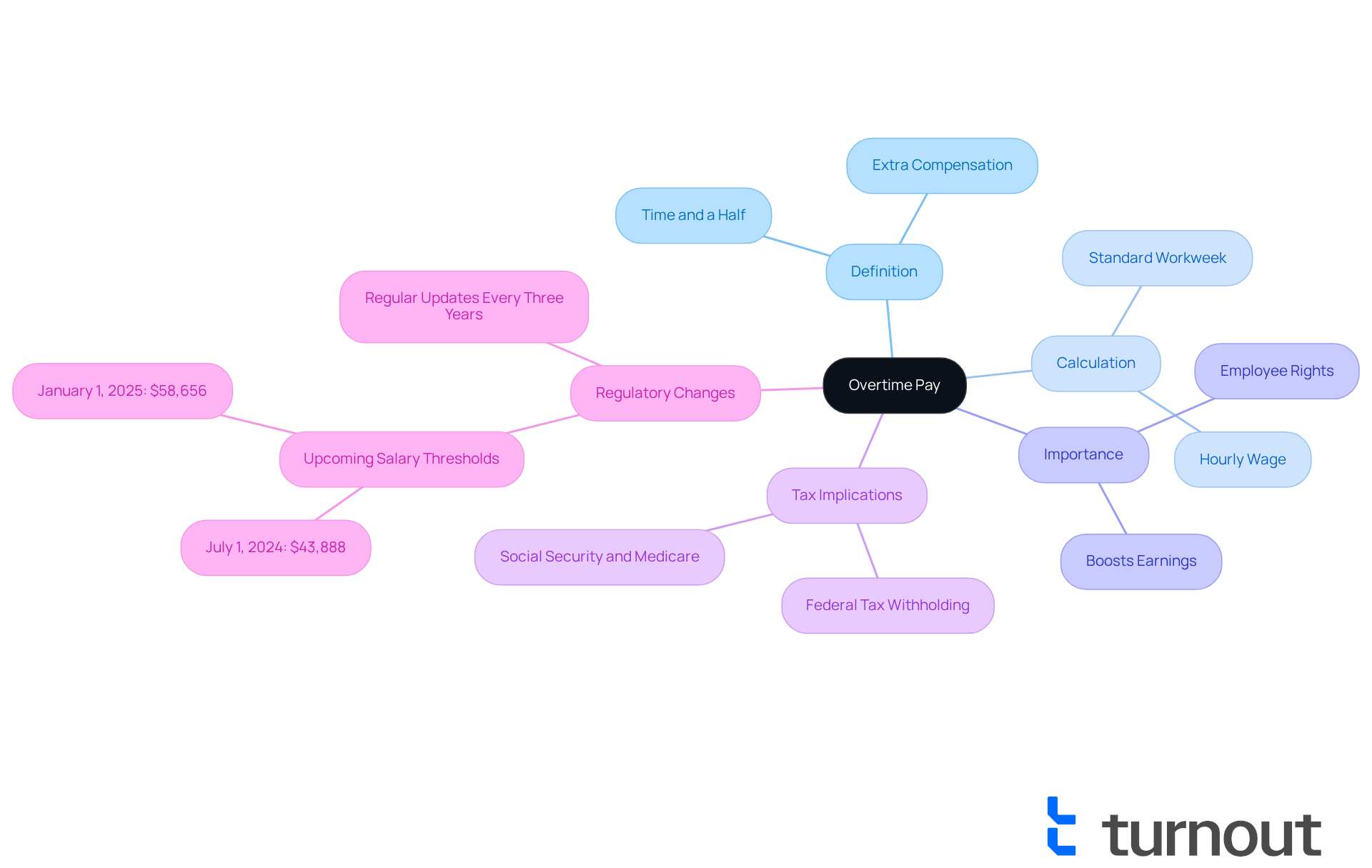
Define Overtime Pay and Its Importance
Overtime pay is the extra compensation that you earn when you work beyond the standard 40 hours in a workweek. Typically, this pay is calculated at a rate of one and a half times your regular hourly wage, often referred to as 'time and a half.' Understanding this additional pay is crucial because it affects your income and has important implications for tax calculations, especially concerning the tax rate for overtime pay and your overall financial strategy.
For many employees, especially those in hourly positions, extra hours can significantly boost earnings. This makes it an essential part of your compensation package. We understand that knowing how extra work hours are defined and calculated can empower you to advocate for your rights and ensure you receive fair compensation for the time you put in.
With upcoming changes to salary thresholds for overtime eligibility—set to increase to $43,888 on July 1, 2024, and to $58,656 on January 1, 2025—it's vital to stay informed about your rights and the potential financial benefits of overtime pay. As Julie Su, Acting Secretary of the US Department of Labor, stated, 'This rule will restore the promise to workers that if you work more than 40 hours in a week, you should be paid more for that time.'
Moreover, it's important to remember that the tax rate for overtime pay is subject to federal tax withholding, and Social Security and Medicare taxes still apply. This can impact your overall financial planning. You're not alone in navigating these complexities, and we're here to help you understand your rights and make the most of your hard work.
Debunk Myths About Overtime Taxation
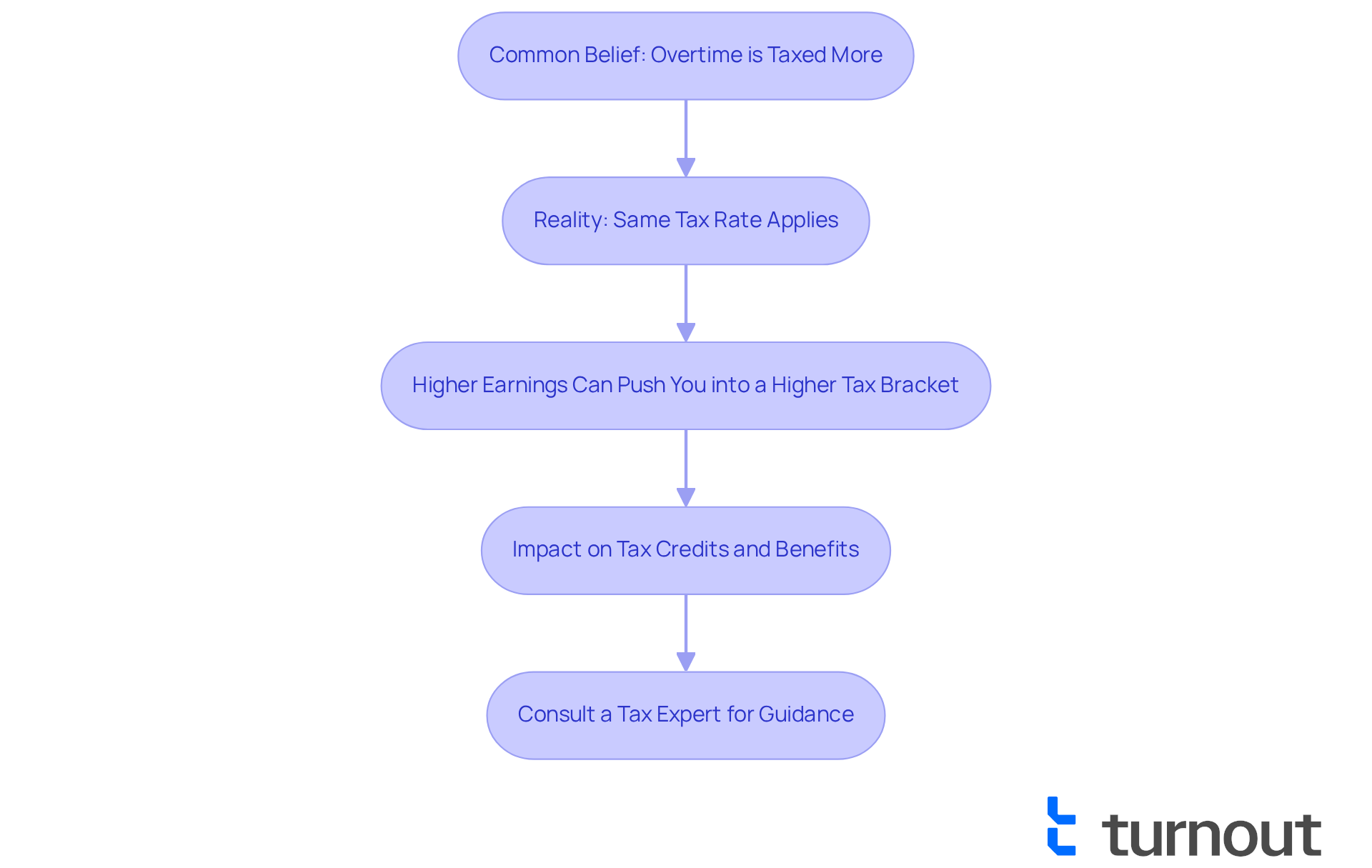
It's common to feel confused about how extra hours of work affect your pay. Many people believe that the tax rate for overtime pay is higher than the tax rate for regular wages. In reality, both extra work compensation and standard earnings are subject to the tax rate for overtime pay, as they fall under the same federal tax rates. However, when you work additional hours, it can elevate your overall earnings, potentially pushing you into a higher tax bracket. This can create the impression that you're being taxed more heavily.
Surveys show that a significant number of employees think their extra earnings are taxed at a higher rate. It’s essential to understand that there is no separate 'extra hours tax'; all earnings, including those from extra hours, are taxed at the tax rate for overtime pay just like regular earnings. Tax professionals stress that recognizing these myths can help you manage your expectations about take-home pay and tax obligations. This understanding allows for more effective financial planning.
For instance, if your usual earnings place you in the 12% tax bracket, any extra compensation from additional hours could be taxed at 22%. But remember, only the amount that exceeds the threshold is taxed at that higher rate. Additionally, increased income from extra work might influence your eligibility for specific tax credits or government benefits.
We understand that navigating these tax implications can be overwhelming. By adjusting your withholding allowances or consulting with a tax expert, you can better prepare for the tax consequences of your additional earnings. You're not alone in this journey; we're here to help you make informed decisions.
Explore Tax Implications of Overtime Pay
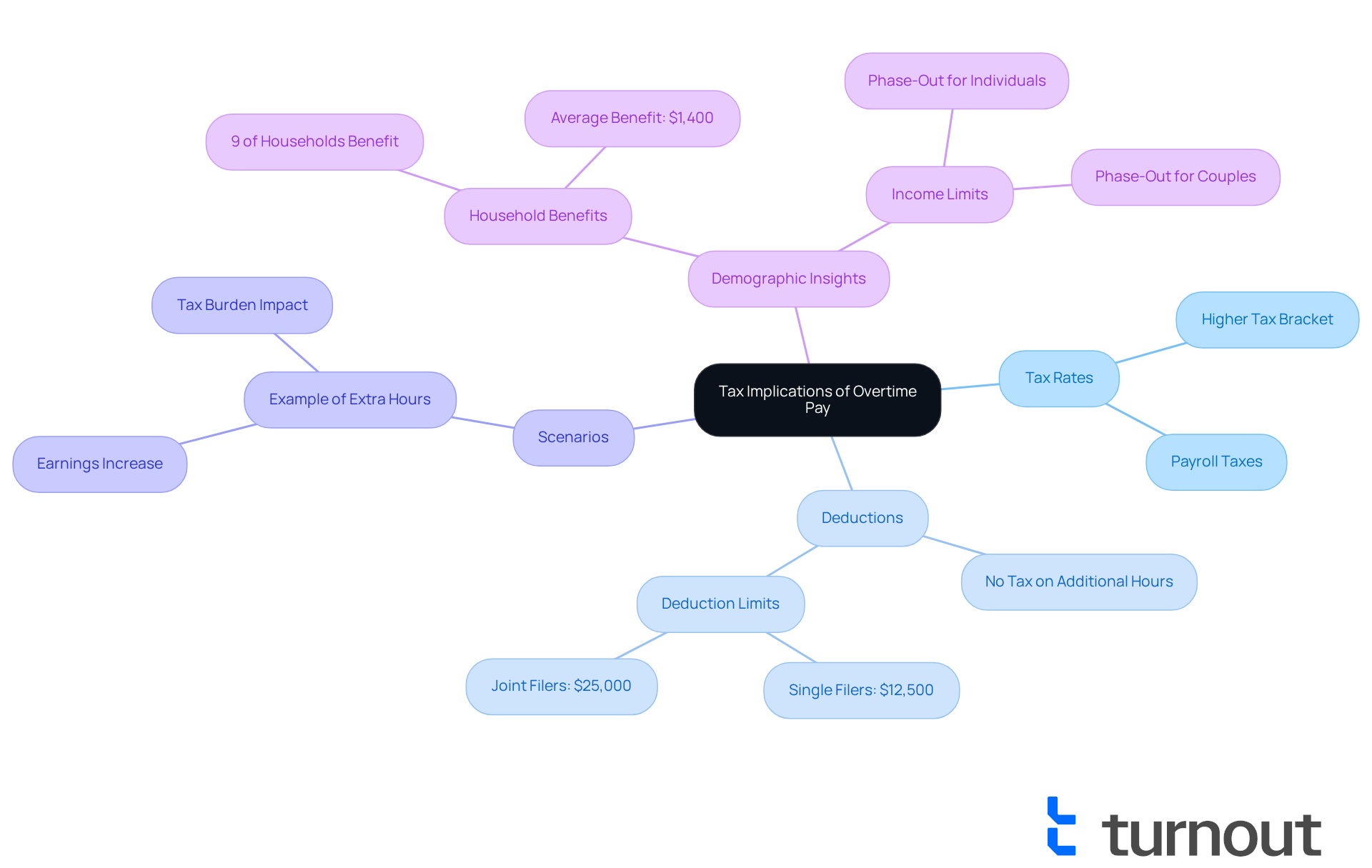
The tax consequences of additional pay can feel overwhelming. While extra earnings are taxed at the same rate as standard earnings, the tax rate for overtime pay can increase your total taxable revenue, possibly pushing you into a higher tax bracket. This means that while you may earn more through additional hours, you could also face a higher tax rate for overtime pay, leading to an increased tax burden.
Thankfully, recent legislative changes, such as the 'No Tax on Additional Hours' provision, allow qualified workers to subtract a portion of their extra pay from their taxable earnings. Specifically, you can subtract up to $12,500 in eligible extra pay ($25,000 for joint filers) from your federal tax obligations. This deduction is set to begin in the 2025 tax year and continue through 2028, aimed at easing some of the tax burdens associated with the tax rate for overtime pay and increased earnings from extra hours worked. It’s essential to understand how to take advantage of these benefits.
Consider this: if you’re an employee making $40 an hour and you record extra hours, your taxable earnings might increase significantly. For instance, working 10 extra hours in a week could boost your earnings by $600, which, depending on your total income, might subject you to a higher tax rate for overtime pay. This scenario highlights the importance of managing additional earnings and understanding the tax rate for overtime pay. Financial consultants often recommend keeping detailed records of extra hours and compensation to navigate these changes effectively and maximize possible deductions during tax season.
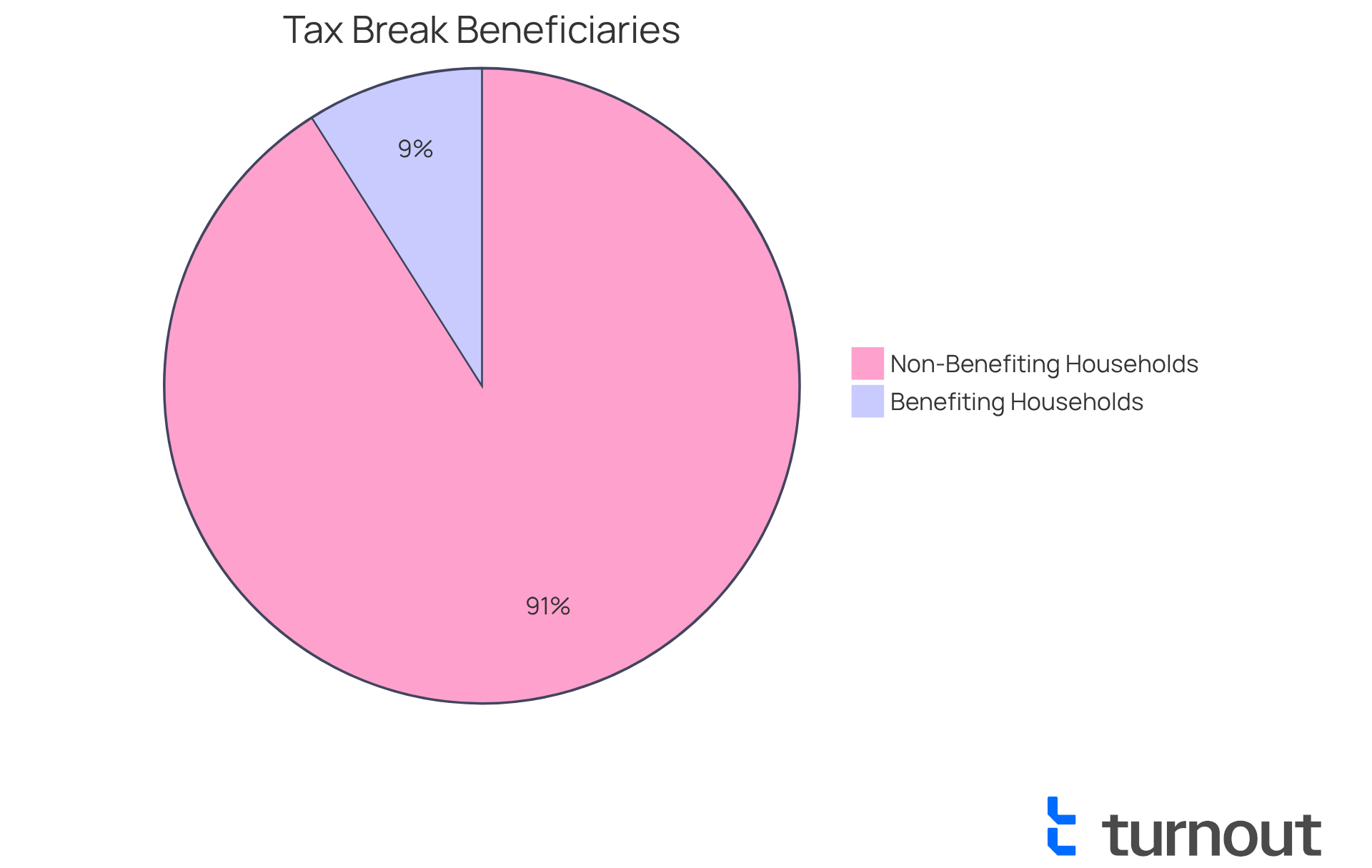
It’s important to recognize that only 9% of American households will benefit financially from the extra pay tax exemption, with an average yearly benefit of approximately $1,400. Additionally, payroll taxes, including Social Security and Medicare, still apply to extra pay. The deduction decreases for individuals with adjusted gross earnings exceeding $150,000 and for married couples with earnings above $300,000. Moreover, married couples must file jointly to qualify for the deduction, which can significantly impact tax strategies for couples.
We understand that navigating these tax implications can be challenging, but you are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you make sense of it all and ensure you’re taking full advantage of available benefits.
Analyze Recent Legislative Changes Impacting Overtime Taxation
Recent legislative changes, particularly the 'One Big Beautiful Bill Act,' have brought significant modifications to the tax rate for overtime pay. Starting January 1, 2025, qualifying staff can deduct up to $12,500 of their additional earnings from their taxable income, a provision that remains in effect until December 31, 2028. This deduction specifically pertains to compensation for extra hours worked beyond the standard pay rate, providing a financial benefit to employees who depend on additional hours to enhance their income. For married couples, the maximum deduction is set at $25,000. However, it's important to note that this advantage is subject to earnings thresholds, phasing out for individuals earning over $150,000 and couples making over $300,000.
We understand that navigating tax laws can be daunting, but staying informed is crucial as these changes can directly influence your financial outcomes. The legislation aims to create nearly one million new jobs while offering tax relief to the middle class. On average, taxpayers are expected to see a reduction of approximately $3,752 in their tax burden. However, only 9% of American households are projected to benefit from this tax break, resulting in an average added windfall of roughly $1,400 annually.
It's common to feel overwhelmed by these new regulations, particularly because the tax rate for overtime pay affects not all extra hours. The deduction specifically relates to qualifying additional wage payments under defined income limits. To benefit from this deduction, employees must ensure that their employers report additional earnings separately on W-2 forms. Additionally, the Economic Policy Institute has raised concerns that this law may inadvertently encourage excessive overtime work, potentially impacting workers' physical and mental health.
As the landscape of tax deductions evolves, we want you to know that understanding these provisions will be crucial for maximizing your financial benefits during tax season. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we're here to help you navigate these changes and make the most of your hard work.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of overtime pay and its tax implications is essential for anyone looking to maximize their earnings and navigate the complexities of their financial landscape. We know that overtime pay, calculated at a rate of one and a half times the regular hourly wage, not only enhances income but also carries significant tax responsibilities that can affect your overall financial health. With upcoming changes to salary thresholds and tax deductions, staying informed empowers you to advocate for your rights and optimize your compensation strategies.
This article highlights key aspects of overtime pay, including:
- Common misconceptions about overtime taxation
- The impact of increased earnings on tax brackets
- Recent legislative changes that offer potential tax relief
It's common to feel confused about the taxation of extra hours, but debunking these myths clarifies that all earnings are subject to the same tax rates. New provisions also allow eligible workers to deduct a portion of their overtime income from taxable earnings. This understanding is crucial for effective financial planning, especially as the landscape of tax deductions evolves.
Ultimately, being proactive about overtime pay and its tax implications can lead to better financial outcomes. We encourage you to:
- Stay informed about your rights
- Consult with tax professionals
- Keep detailed records of your work hours and earnings
By doing so, you can ensure you are making the most of your hard work and navigating the complexities of taxation with confidence. Embracing this knowledge not only empowers you but also fosters a more equitable workplace where fair compensation is prioritized.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is overtime pay?
Overtime pay is the extra compensation earned when you work beyond the standard 40 hours in a workweek, typically calculated at one and a half times your regular hourly wage, known as 'time and a half.'
Why is understanding overtime pay important?
Understanding overtime pay is crucial because it affects your income, tax calculations, and overall financial strategy. It empowers you to advocate for your rights and ensure fair compensation for extra hours worked.
How can overtime pay impact my earnings?
For many employees, especially those in hourly positions, extra hours can significantly boost earnings, making overtime an essential part of the compensation package.
What are the upcoming changes to salary thresholds for overtime eligibility?
The salary thresholds for overtime eligibility are set to increase to $43,888 on July 1, 2024, and to $58,656 on January 1, 2025.
What did Julie Su, Acting Secretary of the US Department of Labor, say about overtime pay?
Julie Su stated that the upcoming rule will restore the promise to workers that if they work more than 40 hours in a week, they should be paid more for that time.
How does overtime pay affect taxes?
Overtime pay is subject to federal tax withholding, and Social Security and Medicare taxes apply, which can impact your overall financial planning.




