Overview
We understand that navigating tax filing can feel overwhelming, especially if you didn't work this year. However, it's important to consider filing your taxes, as it may open the door to valuable tax credits and refunds. For instance, you could be eligible for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the Child Tax Credit, which can significantly ease your financial burden.
If you've had taxes withheld or received unemployment benefits, filing could be particularly beneficial for you. Understanding your eligibility for these financial supports is crucial, and we're here to help you through this process. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and taking this step could lead to unexpected support during challenging times.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax season can feel particularly daunting, especially for those who have not worked throughout the year. We understand that the question of whether to file taxes despite having no income is more than just an obligation; it opens the door to potential benefits and credits that could significantly enhance your financial situation.
With various income thresholds and eligibility criteria for tax credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit and Child Tax Credit, understanding these nuances is essential. It's common to feel overwhelmed, but what if filing a return—even without earnings—could unlock financial support that many overlook? You are not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you explore your options.
Determine Your Filing Requirement Based on Income Status
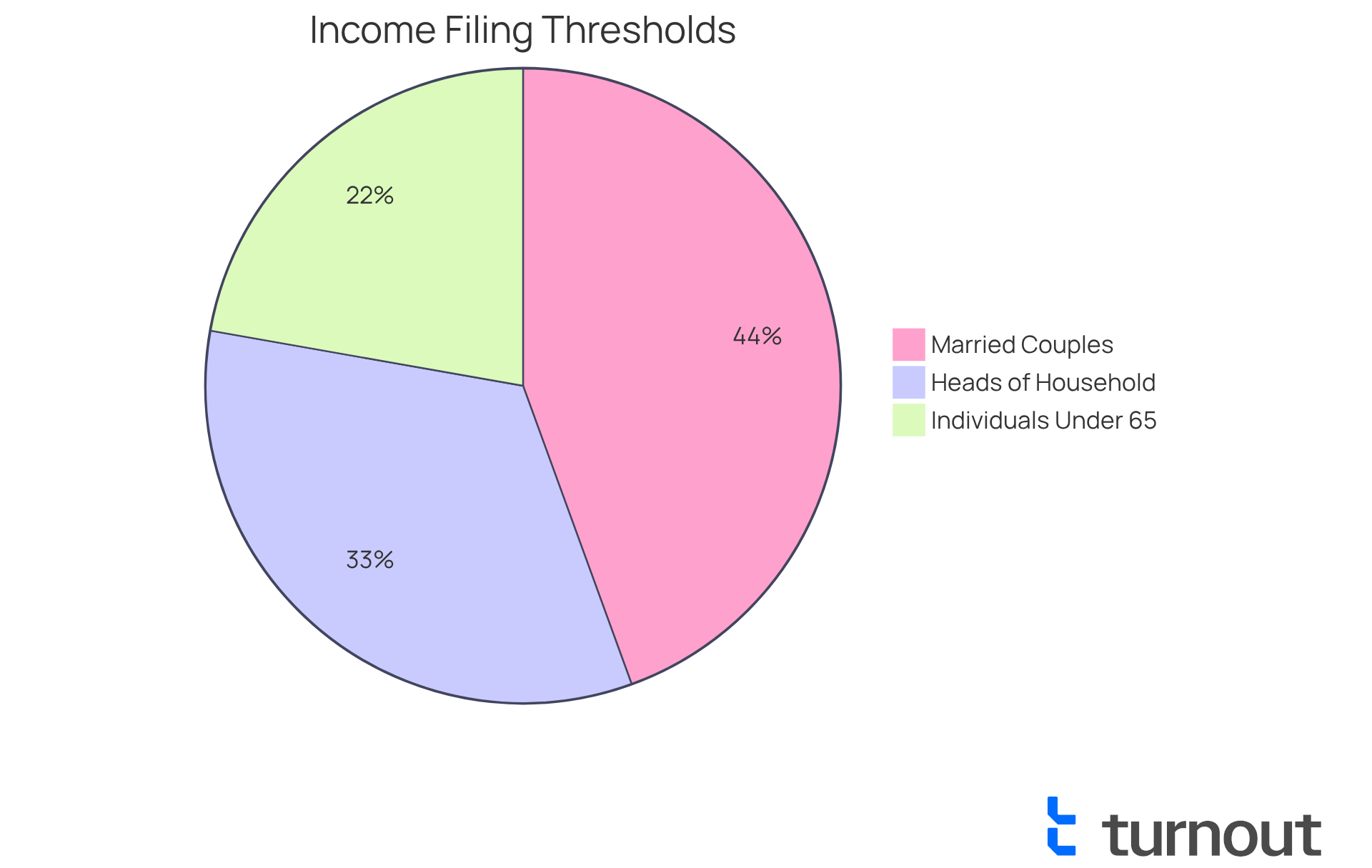
We understand that navigating tax season can be overwhelming. First, verify if your gross income exceeds the minimum limit for your status. For the 2024 tax year, this is $14,600 for individuals under 65. If you're a head of household, the threshold is $21,900, and for married couples filing jointly, it stands at $29,200 if both partners are under 65.
It's essential to consult IRS guidelines to ensure you meet the criteria for mandatory submission. These requirements can vary based on your age and tax status, and we want to help you understand them fully.
Consider any special situations that may apply to you. Even if your earnings are beneath the threshold, it raises the question: should I file taxes if I didn't work? This includes instances where you might wonder, should I file taxes if I didn't work, to see if you could be eligible for specific tax benefits or have had taxes deducted from your paychecks. Filing a return could lead to potential refunds or credits, especially if you received unemployment benefits or had federal income tax withheld.
We encourage you to utilize tools like the Interactive Tax Assistant. This resource can help you evaluate your specific situation and establish your reporting obligations based on your unique circumstances. It’s designed to provide answers to common tax law questions while keeping your information anonymous and secure.
Remember, submitting on time or asking for an extension is crucial to avoid penalties, even if you're unable to pay the complete amount due. You're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you every step of the way.
Evaluate Income Thresholds and Types of Income
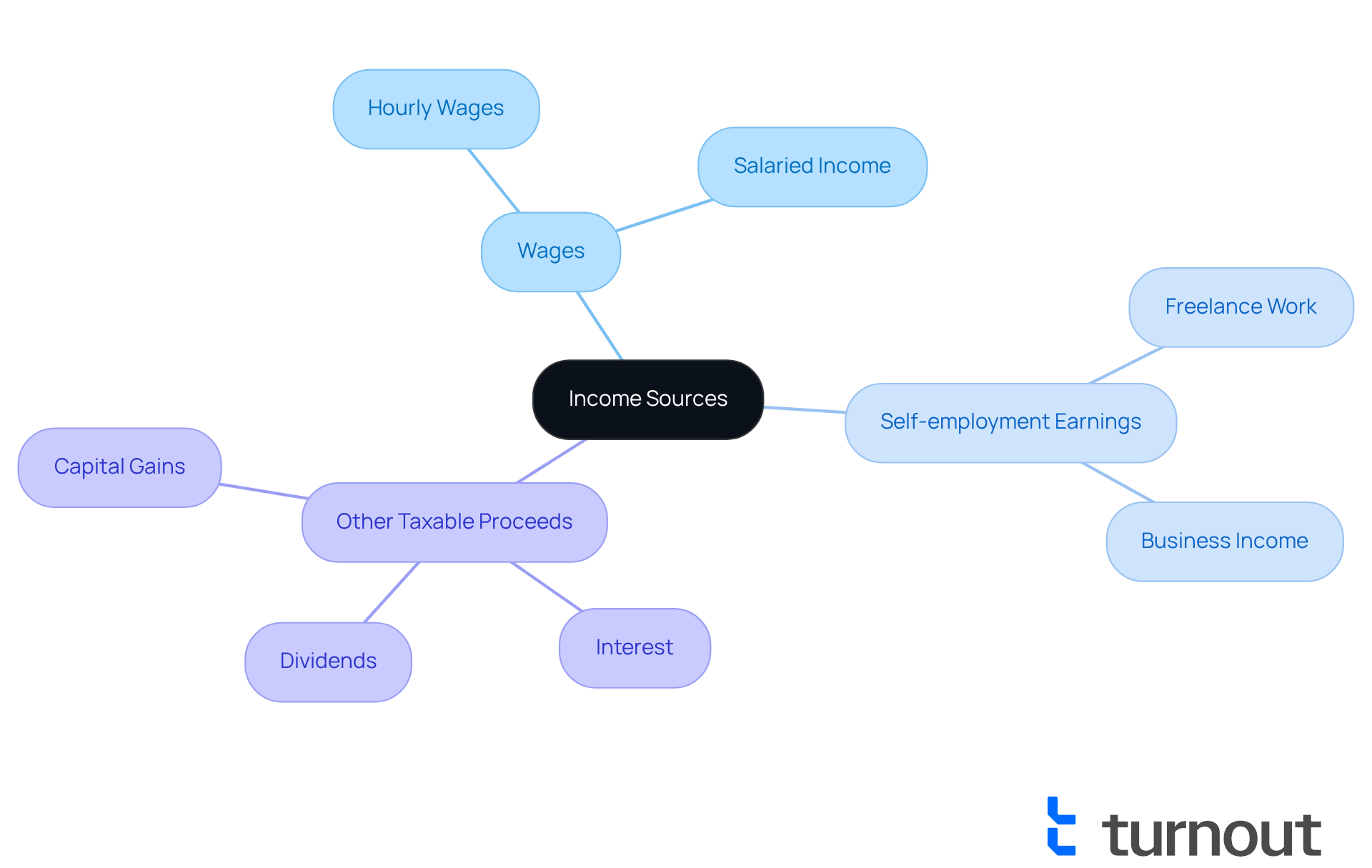
We understand that navigating your finances can be overwhelming. To ease this process, it's essential to identify all sources of revenue, including:
- Wages
- Self-employment earnings
- Any other taxable proceeds
By doing so, you can gain clarity on your financial situation.
It's common to wonder how different types of revenue, like interest, dividends, or capital gains, might affect your filing requirements. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed decisions.
To support you further, we encourage you to utilize IRS resources. These tools can help you locate specific revenue thresholds for various categories, ensuring you have the information you need to move forward with confidence. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
Consider Eligibility for Tax Credits and Benefits
Explore the available tax incentives, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and Child Tax Credit, to understand your eligibility. These funds can provide significant financial support, even for those without taxable earnings. For instance, the EITC can offer up to $7,430 for qualifying taxpayers in 2024, depending on family size and income level. Importantly, under the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA), the maximum credit for childless workers increased from $543 to $1,502.
Evaluate your eligibility based on your earnings and family size. The EITC is designed for individuals with low to moderate incomes, and eligibility criteria include having a valid Social Security number and earned income below $10,300 (this includes investment income). Additionally, for 2025, the Child Tax Credit (CTC) requires that eligible children be under 17 at the end of the tax year, and your annual income must not exceed $200,000 ($400,000 for joint filers) to receive the full benefit. The CTC gradually phases out at these income levels, so it’s crucial to be aware of your financial limits.
You might wonder, should I file taxes if I didn't work, but consider filing a tax return to claim refundable benefits, even if you have no taxable income. Many eligible individuals miss out on these benefits, losing the opportunity for potential refunds that could improve their financial situation. Turnout can support you in navigating these processes with trained nonlawyer advocates and IRS-licensed enrolled agents, ensuring you grasp your eligibility for these benefits. Filing a return allows you to access these credits, which can greatly enhance your overall financial support. Please note that EITC claims may face delays in tax refunds, as the IRS is required to hold refunds for EITC claims until mid-February. Remember, Turnout is not a law firm and does not provide legal representation.
Collect Required Documentation for Tax Filing
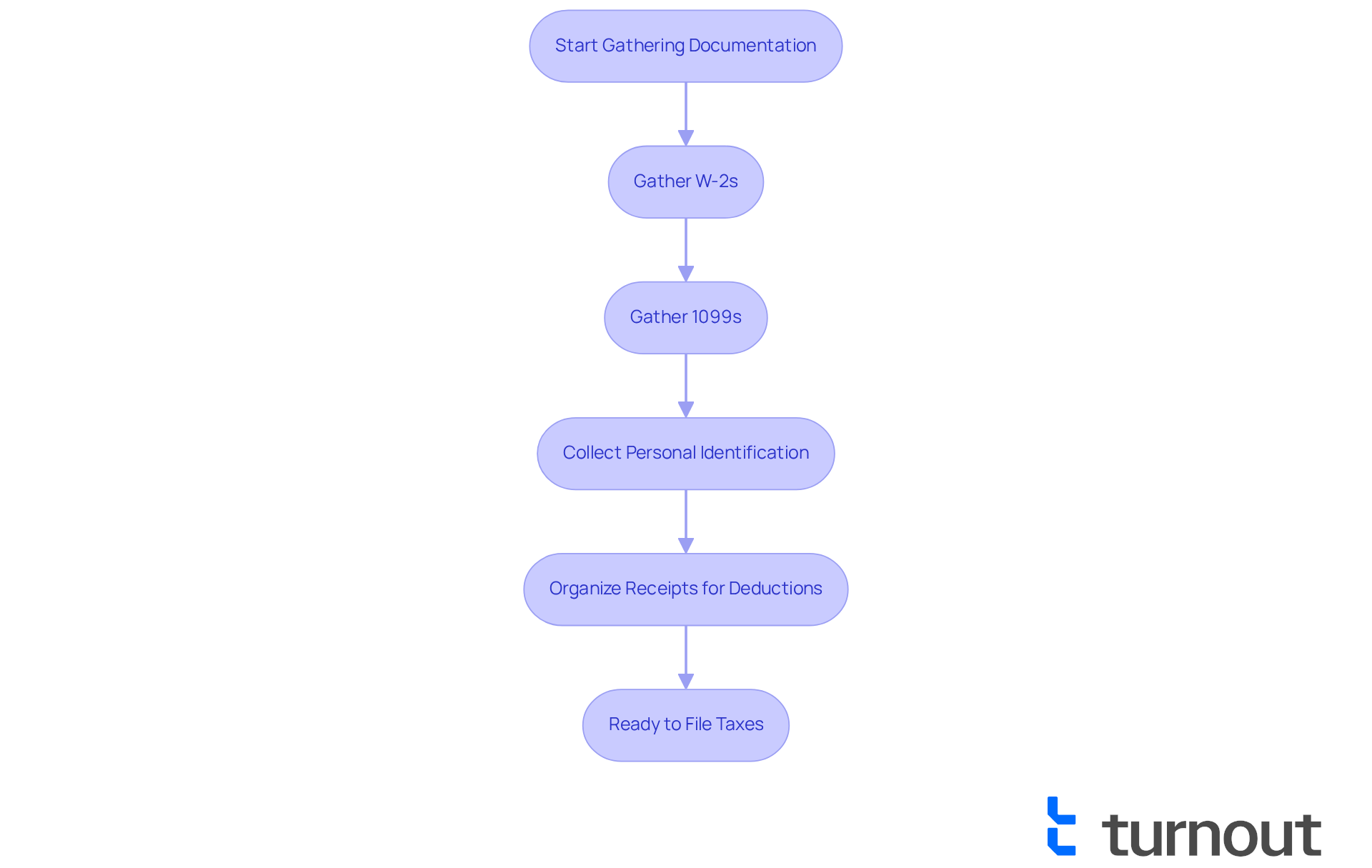
Filing your taxes can feel overwhelming, especially when you are wondering, should I file taxes if I didn't work or if you're unemployed and seeking benefits. We understand that compiling all relevant documents is crucial. Start by gathering your W-2s, 1099s, and any other income statements that reflect your financial situation. Don't forget to collect personal identification information, such as Social Security numbers for yourself and any dependents.
Organizing receipts and records for deductions or credits you plan to claim is essential. Remember, you are not alone in this process. Turnout is not a law firm and does not provide legal advice, but our trained nonlawyer advocates are here to assist you in navigating the SSD claims process. Additionally, our IRS-licensed enrolled agents are ready to support you with tax debt relief.
Together, we ensure you comprehend the requirements and have the essential documentation for your tax submission. We're here to help you every step of the way.
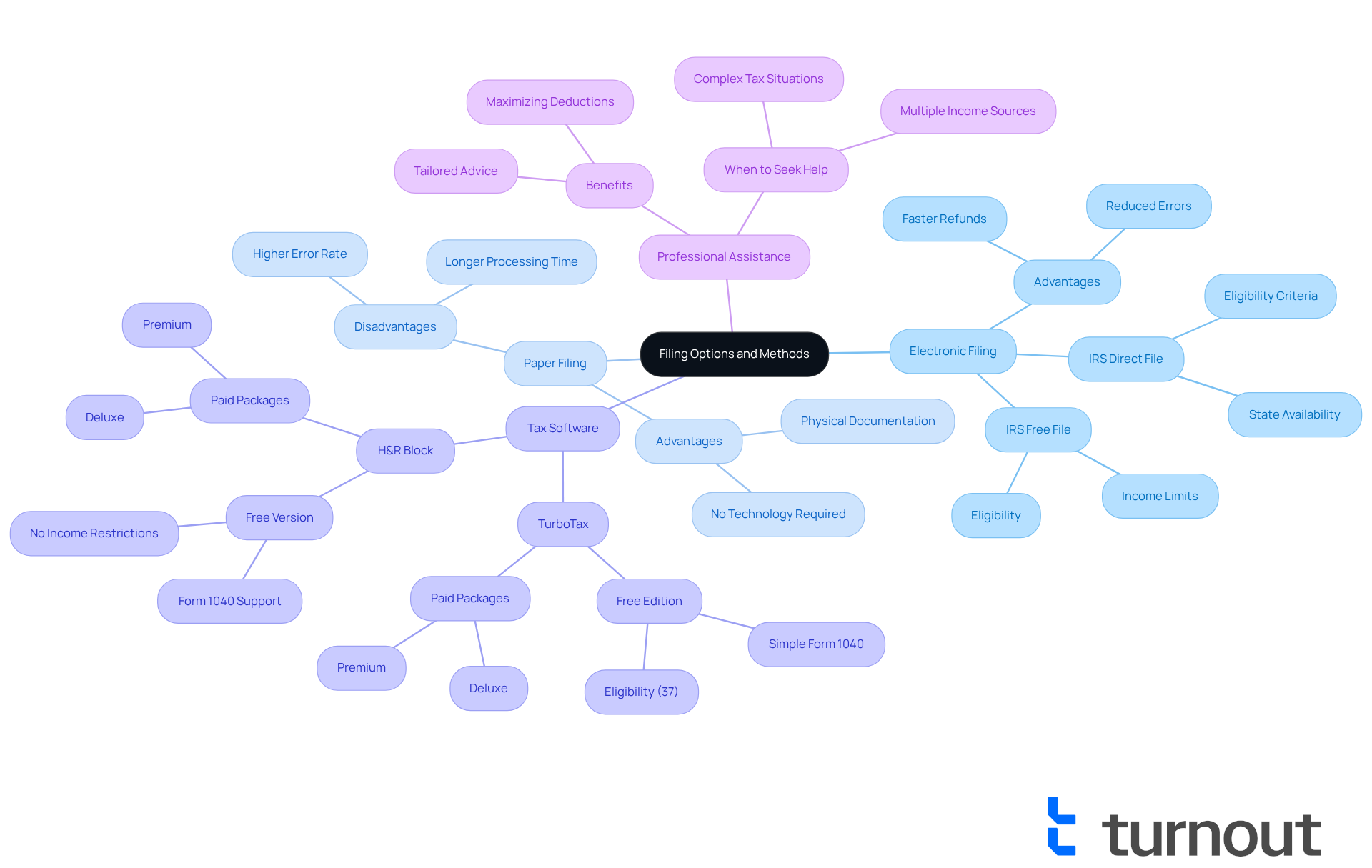
Understand Filing Options and Methods
When deciding how to file your taxes, we understand that it can feel overwhelming. Consider whether to use electronic methods or traditional paper forms based on your comfort level and available resources. Electronic submission is generally quicker and more efficient, with the IRS usually issuing refunds within 21 days for e-filed returns, compared to up to six weeks for paper submissions.
Explore different tax preparation software options that can streamline the submission process. For instance, TurboTax is recognized for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive support, making it a top choice for many filers. Its Free Edition allows eligible taxpayers to file both federal and state returns at no cost, catering to those with simple tax situations; approximately 37% of tax filers qualify for this option. Likewise, H&R Block provides comprehensive live assistance and a complimentary version that manages basic tax forms without earnings limitations.
If your tax situation is complex, it’s common to feel uncertain about the next steps. Consider seeking assistance from a tax professional. While tax software can guide you through the filing process, professionals can provide tailored advice for intricate scenarios, ensuring you maximize your deductions and credits.
Looking ahead to 2025, the landscape of tax preparation continues to evolve. Options like IRS Free File and IRS Direct File are available for qualifying taxpayers, enabling them to submit their taxes at no cost. However, it's essential to acknowledge that IRS Free File has earnings limits, and IRS Direct File is only accessible in specific states. This emphasizes the significance of assessing your individual situation to identify the most suitable submission method for you. Remember, we're here to help you navigate this journey.
Review and Double-Check Your Tax Return
We understand that reviewing your tax return can feel overwhelming. It's essential to carefully review all entries for accuracy, including income amounts and deductions. Ensuring that all required forms are included and properly filled out is crucial for a smooth process.
Consider having a second pair of eyes review your return. Sometimes, a fresh perspective can catch potential errors that we might overlook. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate through it with confidence.
File Your Tax Return Before the Deadline
We understand that tax season can be stressful, and it's important to stay organized. Mark the tax filing deadline on your calendar—April 15, 2025, for most taxpayers. This simple step can help you avoid last-minute rushes.
When it comes time to submit your tax return, remember that you can do so electronically or ensure it is postmarked by the deadline. This option can make the process smoother and more efficient.
If you find that you cannot file on time, it's common to feel overwhelmed. Consider applying for an extension. This can help you avoid penalties and give you the extra time you need to prepare your return accurately. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
Conclusion
Deciding whether to file taxes when you haven’t worked can feel overwhelming, but it’s important to understand your tax obligations. While filing may not be mandatory for everyone, particularly those below certain income thresholds, it can still offer significant benefits. Engaging with the tax system could reveal potential refunds and credits that many individuals overlook. This makes it worthwhile to consider filing, even if you have no earnings.
We know that assessing your income status against filing requirements can be confusing. It’s essential to explore your eligibility for valuable tax credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit and Child Tax Credit. Gathering the necessary documentation to support your tax return is crucial, and utilizing resources such as IRS guidelines and tax preparation tools can simplify the process and help ensure compliance with regulations.
Ultimately, the importance of filing taxes, even for those without income, cannot be overstated. It opens up opportunities for financial support that can truly enhance your situation, especially through refundable credits. By taking proactive steps to understand and navigate your tax obligations, you empower yourself to make informed decisions, ensuring you don’t miss out on potential benefits. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey—embrace the opportunity to engage with the tax system and consider filing your return. It may lead to unexpected financial relief.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I determine if I need to file taxes based on my income?
You need to verify if your gross income exceeds the minimum limit for your filing status. For the 2024 tax year, the thresholds are $14,600 for individuals under 65, $21,900 for heads of household, and $29,200 for married couples filing jointly if both are under 65.
What should I do if my income is below the filing threshold?
Even if your income is below the threshold, you may still want to file taxes to check for eligibility for tax benefits or refunds, especially if you had taxes withheld or received unemployment benefits.
What resources can help me understand my tax filing requirements?
The IRS provides resources like the Interactive Tax Assistant, which can help you evaluate your specific situation and determine your reporting obligations while keeping your information secure.
What types of income should I consider when evaluating my filing requirements?
You should identify all sources of revenue, including wages, self-employment earnings, and any other taxable proceeds.
How do different types of income affect my tax filing requirements?
Different types of income, such as interest, dividends, or capital gains, can impact your filing requirements. Understanding these nuances is important for making informed decisions about your taxes.
What should I do if I cannot pay the full amount due on my taxes?
It's crucial to submit your tax return on time or request an extension to avoid penalties, even if you're unable to pay the full amount due.




