Overview
POTS, or Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome, can indeed be viewed as a disability. This is particularly true when it significantly hinders an individual's ability to perform work-related tasks. Many individuals experience debilitating symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and cognitive challenges.
We understand that navigating daily life with POTS can be incredibly challenging. It's essential to have thorough medical documentation and personal narratives that illustrate how POTS affects your everyday experiences. This documentation is crucial for establishing eligibility in the Social Security Disability claims process.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you through the process and ensure your voice is heard. Taking these steps can make a significant difference in your path to obtaining the support you deserve.
Introduction
The complexities surrounding Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) can leave many feeling uncertain about its status as a disability. With symptoms that often lead to debilitating fatigue and cognitive difficulties, it's common to question how one might navigate the challenging path toward securing disability benefits.
This article aims to provide clarity and support as we explore the critical steps to determine whether POTS qualifies as a disability. We will offer insights into the necessary documentation and discuss the challenges that may arise during the application process.
You are not alone in this journey—together, we will uncover whether those suffering from this condition can find the support they need or if they will face barriers that complicate their quest for assistance.
Understand Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
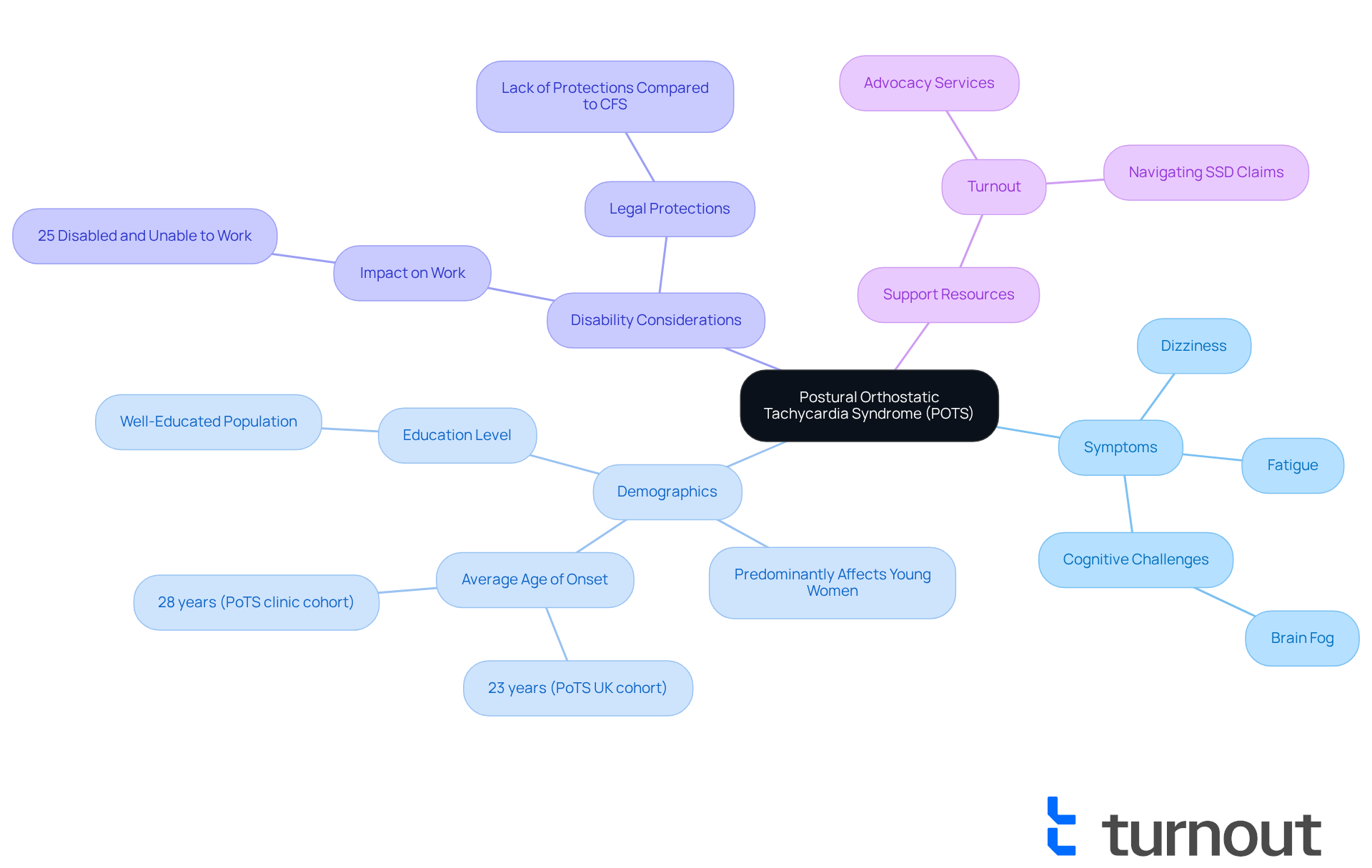
Many people wonder if POTS is a disability, as it is a condition that can lead to a significant rise in heart rate when standing, resulting in various debilitating effects. Many individuals experience dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, and cognitive challenges often referred to as 'brain fog.' These symptoms can severely limit daily activities, such as bathing, household chores, and even basic mobility, making it difficult to maintain steady work abilities.
It's important to recognize that this condition predominantly affects young, well-educated women, with many facing significant morbidity comparable to chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Approximately 25% of those with POTS find themselves disabled and unable to work, raising the question of whether POTS is a disability, which underscores its profound impact on quality of life. Additionally, patients often endure a lengthy diagnostic process, which can worsen their condition and delay access to essential support.
Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of acknowledging the debilitating nature of this condition. One expert noted that individuals with POTS encounter challenges similar to those with CFS, yet they lack the same legal protections. This discrepancy can lead to misdiagnosis, with many patients mistakenly identified as having anxiety or chronic fatigue syndrome.
Understanding how POTS impacts daily life is crucial for those considering if POTS is a disability for eligibility in disability benefits. The first step is recognizing the symptoms and their impact on work capabilities, as these factors significantly influence eligibility for assistance. Turnout provides valuable tools and services, including trained non-professional advocates, to help individuals navigate the complexities of SSD claims. This ensures that those affected by POTS can access the support they need without requiring legal representation. It's essential to note that Turnout is not a law firm and does not offer legal representation.
As one specialist highlighted, "We would recommend that raising awareness of this debilitating condition is crucial to enhance understanding, diagnosis, and management of this illness." You are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you find the support you deserve.
Review Diagnostic Criteria for POTS
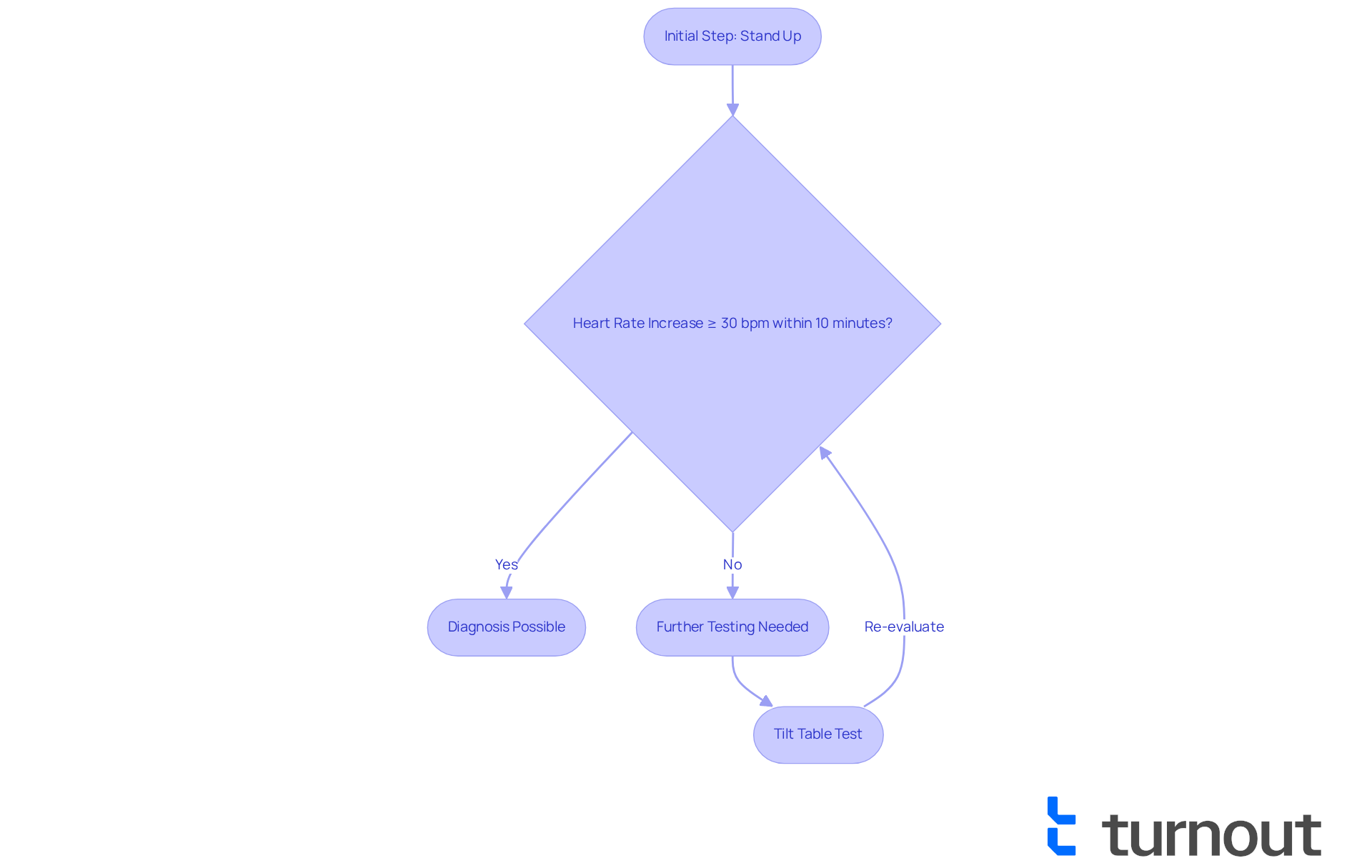
Receiving a diagnosis of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome can feel overwhelming. To qualify, a patient typically needs to demonstrate a heart rate increase of at least 30 beats per minute (bpm) within 10 minutes of standing, or a heart rate that exceeds 120 bpm upon standing. We understand that navigating this process can be challenging, and additional tests like the tilt table test may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
It's crucial to grasp these standards, especially for those who are seeking to define their situation as POTS a disability. You will need to provide this information in your applications. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Turnout can assist those diagnosed with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome in understanding if POTS is a disability within the Social Security Disability (SSD) claims process. We are here to ensure you have the necessary support and guidance to effectively present your case.
Evaluate Eligibility for Disability Benefits with POTS
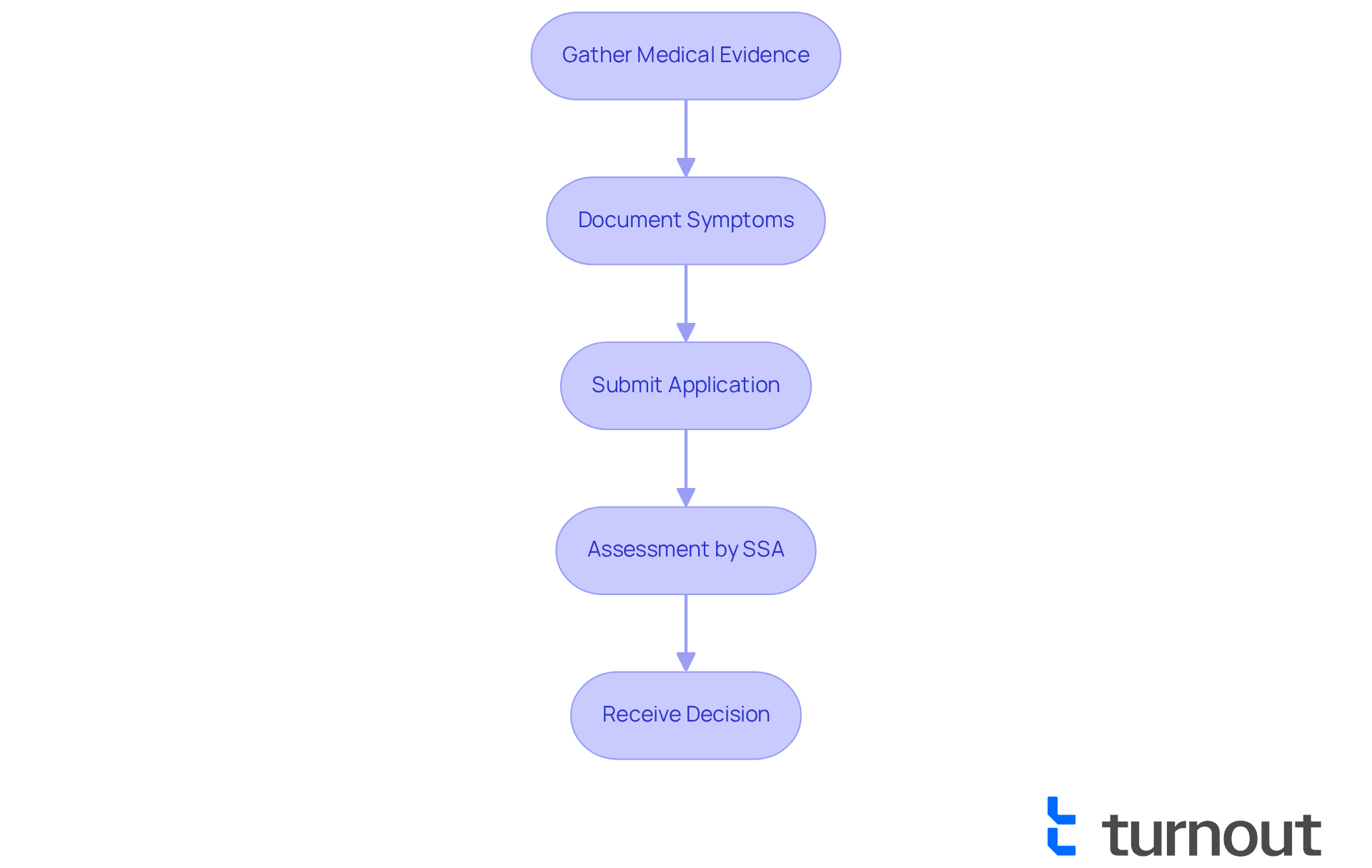
To qualify for disability benefits due to Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome, it's essential to demonstrate how this condition significantly impacts your ability to perform work-related tasks. Unfortunately, the Social Security Administration (SSA) does not have a specific listing for POTS, which means you will need to gather thorough medical evidence showing how your situation affects your daily life and work capabilities. This documentation should detail how symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties make it challenging to maintain employment or complete essential tasks.
We understand that the question of whether POTS is a disability often leads individuals to face hurdles in obtaining disability benefits. The inconsistency of symptoms and the lack of a definitive diagnostic test can lead to skepticism from assessors. Many initial applications for POTS-related benefits are denied, often due to insufficient medical documentation or an inability to clearly demonstrate how symptoms affect work performance. It’s crucial to provide comprehensive documentation of your diagnosis, treatment history, and objective test results, such as tilt table tests, to support your claims.
Turnout emphasizes the importance of thorough documentation and connects applicants with knowledgeable non-legal advocates who can assist in navigating the SSD application process. Please remember that Turnout is not a law firm and does not offer legal advice. Statements from your treating physicians regarding the severity and frequency of your symptoms are vital. Evidence showing how these symptoms limit your daily activities can significantly bolster your claim. As one advocate wisely noted, "The more information you can provide, the better your chances of approval."
Recent updates from the SSA reveal that while POTS is considered a disability under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), individuals can qualify for benefits through a medical vocational allowance. This is possible if you can demonstrate that your residual functional capacity (RFC) is severely limited by your condition. This assessment considers your work history, developed job skills, and overall qualifications, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of how your condition affects your ability to work. Remember, documenting the frequency, duration, and severity of syncope episodes is essential for your SSD application. You're not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
Gather Documentation and Evidence for Your Claim
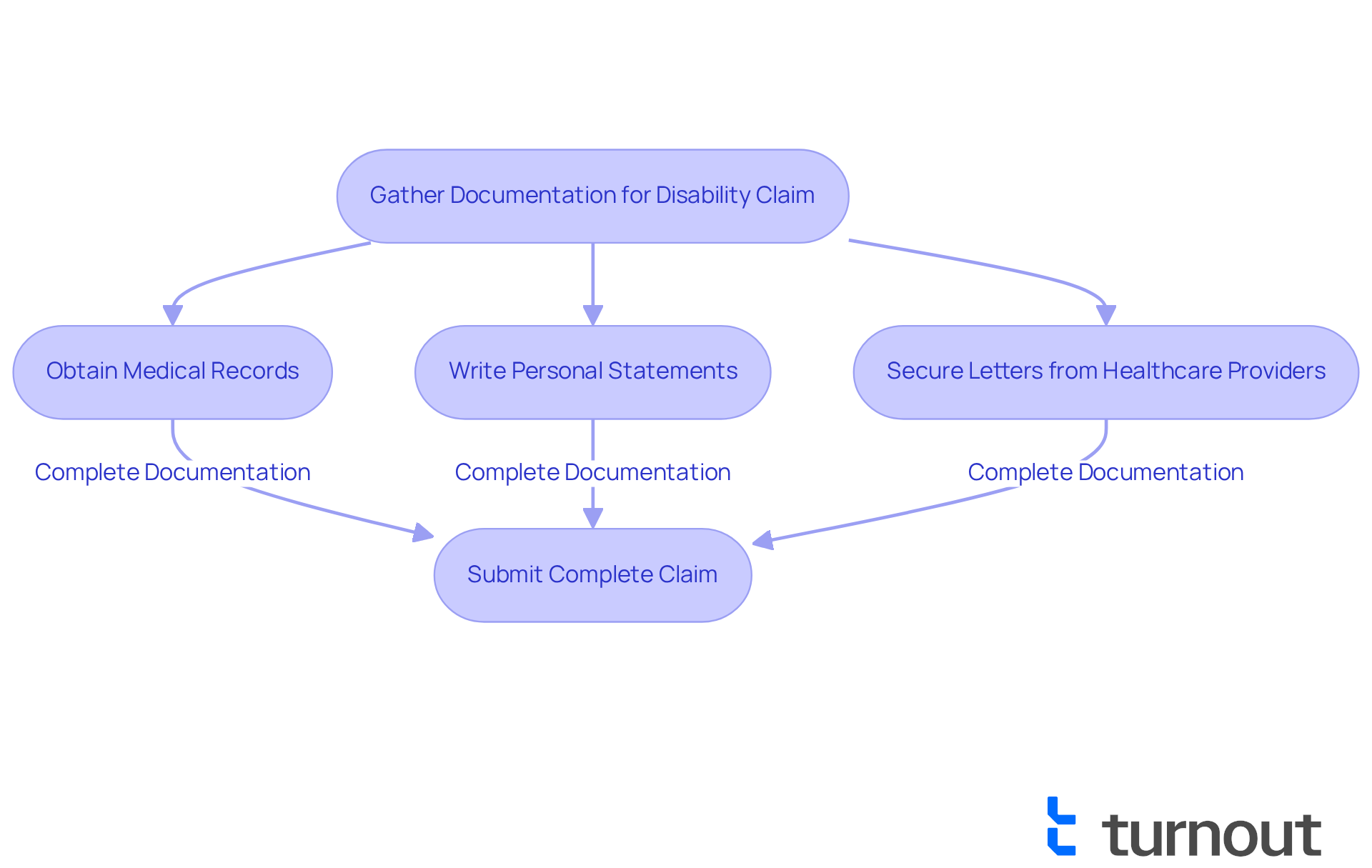
Navigating the process of applying for disability benefits can feel overwhelming, but you are not alone in this journey. To successfully apply, it's essential to compile thorough documentation that substantiates your claim. Here are some key components to consider:
-
Medical Records: Start by obtaining detailed records from your healthcare providers. These should outline your diagnosis, treatment history, and ongoing management, as well as address whether POTS is a disability. Clear medical evidence is vital, especially since over 25% of working Americans are likely to experience a disabling condition during their lifetime.
When evaluating diagnostic test results, it is important to consider whether POTS is a disability, which may include findings from tests such as tilt table tests or heart rate monitoring. These confirm the diagnosis of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome and provide the objective evidence to determine if POTS is a disability, which the Social Security Administration (SSA) needs to assess your eligibility. -
Personal Statements: Write detailed accounts that illustrate why POTS is a disability and how it affects your daily life. Include specific examples of limitations you experience in both work and personal activities, particularly regarding whether POTS is a disability. Personal narratives can significantly enhance understanding of the impact of your condition.
-
Letters from Healthcare Providers: Secure supportive letters from your doctors or specialists to clarify that POTS is a disability. These should describe the severity of your condition and its effect on your ability to work, especially in relation to whether POTS is a disability. Such endorsements are crucial, as medical evidence plays a critical role in the approval process.
Compiling this evidence is essential for presenting a compelling case to the SSA that addresses whether POTS is a disability. We understand that this process can be daunting, but Turnout offers various tools and services to help you. From guidance on documentation to access to trained nonlawyer advocates, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
The time it takes to gather this documentation can vary, but being proactive and organized can help expedite the process. Remember, successful examples of medical record compilations for POTS claims show that thorough preparation can lead to favorable outcomes when addressing the question of whether POTS is a disability. Your journey is important, and comprehensive documentation is a key step in navigating the disability benefits system.
Conclusion
Understanding whether Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) qualifies as a disability is essential for those affected by this debilitating condition. POTS can significantly impair an individual's ability to perform daily activities and maintain employment, leading many to seek disability benefits. Recognizing the profound impact of POTS on quality of life is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. It underscores the need for appropriate support and resources.
The process of determining eligibility for disability benefits related to POTS can feel overwhelming. It's vital to emphasize the importance of thorough documentation and medical evidence. Key insights include:
- The diagnostic criteria necessary for establishing a POTS diagnosis
- The challenges faced in obtaining benefits due to the lack of specific listings by the Social Security Administration (SSA)
- The vital role of personal statements and letters from healthcare providers in supporting claims
By gathering comprehensive documentation, you can better present your case and improve your chances of receiving the assistance you need.
Ultimately, raising awareness about POTS and its disabling effects is paramount for enhancing understanding, diagnosis, and management of the condition. If you are navigating this journey, know that support is available. Organizations like Turnout offer guidance and resources to help you through the complexities of the disability claims process. Empowerment through knowledge and documentation can lead to better outcomes, ensuring that you receive the recognition and support you deserve. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)?
POTS is a condition characterized by a significant rise in heart rate when standing, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, and cognitive challenges often referred to as "brain fog."
Who is primarily affected by POTS?
POTS predominantly affects young, well-educated women, many of whom experience significant morbidity comparable to chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS).
Can POTS be considered a disability?
Yes, approximately 25% of individuals with POTS find themselves disabled and unable to work, highlighting the profound impact of the condition on quality of life.
What symptoms do individuals with POTS experience?
Individuals with POTS may experience dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, cognitive challenges (brain fog), and limitations in daily activities such as bathing, household chores, and mobility.
What challenges do patients with POTS face in the diagnostic process?
Patients often endure a lengthy diagnostic process, which can worsen their condition and delay access to essential support. Many may be misdiagnosed with anxiety or chronic fatigue syndrome.
What support is available for individuals with POTS regarding disability claims?
Turnout provides valuable tools and services, including trained non-professional advocates, to help individuals navigate the complexities of Social Security Disability (SSD) claims without requiring legal representation.
What is the role of awareness in managing POTS?
Raising awareness of POTS is crucial for enhancing understanding, diagnosis, and management of the condition, as highlighted by healthcare professionals.




