Overview
Filing back taxes can be a daunting task, but you can do so for up to six years. If you're hoping to claim a refund, it's important to act within three years of the original due date. We understand that navigating these guidelines can feel overwhelming, but knowing these timeframes is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Many taxpayers may not realize that they could benefit from filing their back taxes. By taking this step, you could potentially reclaim funds that are owed to you. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you understand your options and make the process as smooth as possible.
If you're feeling uncertain, take a moment to reflect on your situation. What could filing back taxes mean for you? It might just be the opportunity to recover some of what you've lost. We encourage you to explore this possibility and take action today.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of back taxes can feel overwhelming, especially for the millions of Americans facing unpaid dues that exceed $125 billion. We understand that the implications of these outstanding payments can lead to severe penalties and financial instability. It's crucial to address these concerns head-on. This article will guide you through the essential steps for filing back taxes, highlighting the timeline and IRS guidelines to help you reclaim your financial footing.
You might be wondering how many years you can file back taxes. It's common to feel anxious about the best strategies to tackle this pressing issue and avoid the pitfalls of late submissions. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you navigate these challenges with care and understanding.
Understand Back Taxes: Definition and Importance
Outstanding dues are amounts owed that remain unpaid after their deadline. These situations often arise from various reasons, such as oversight, financial difficulty, or misunderstandings about payment responsibilities. We understand that the consequences of overdue payments can feel overwhelming. They can lead to significant penalties, accruing interest, and even legal measures from revenue authorities.
In 2025, over 11.23 million Americans owe an astonishing total of more than $125 billion in unpaid dues. This statistic highlights the extensive nature of this challenge. The repercussions of not addressing overdue payments can be severe. They may include:
- Wage garnishments
- Liens
- Forfeiture of assets
For instance, individuals who neglect their tax responsibilities might face increased scrutiny from the IRS. The agency has ramped up efforts to pursue high-income non-filers and ensure compliance. Real-life examples show the effects of unpaid dues: families may experience financial instability, and individuals might find it difficult to secure loans or mortgages due to their obligations.
Swiftly addressing overdue payments not only helps reduce these repercussions but also reinstates adherence to financial regulations. This enables individuals to reclaim control over their economic futures. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
Identify IRS Guidelines for Filing Back Taxes
The IRS allows taxpayers to understand how many years they can file back taxes for a period of up to six years. We understand that navigating tax obligations can be stressful, especially when you might be eligible for a refund. It is crucial to file within three years of the original due date to claim it. The IRS expects all past-due returns to be filed, and neglecting this obligation can lead to penalties.
It's important to note that around 70 percent of qualifying individual taxpayers earn less than $100,000 each year. This highlights the significance of comprehending tax obligations, particularly for individuals who might be financially at risk. Recent IRS updates indicate that failure-to-pay penalties will resume on April 1, 2024, for eligible taxpayers, particularly those with assessed tax under $100,000. This penalty relief could benefit nearly 5 million taxpayers, providing an estimated $1 billion in tax relief.
To avoid complications, we encourage you to review IRS guidelines or consult a qualified tax professional for the most current information and specific requirements related to your circumstances. Successful cases of taxpayers handling overdue tax submissions illustrate that with the appropriate support and comprehension of IRS regulations, individuals can efficiently manage their tax responsibilities and understand how many years can you file back taxes to possibly obtain refunds.
Furthermore, it's essential to recognize that delays in submission can affect loan approvals. Financial institutions often require copies of submitted tax returns for home purchases, business loans, or federal aid applications. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help you navigate these challenges.
Gather Required Documents for Filing
Filing back taxes can feel overwhelming, but gathering some key documents can make the process smoother. Here’s what you’ll need:
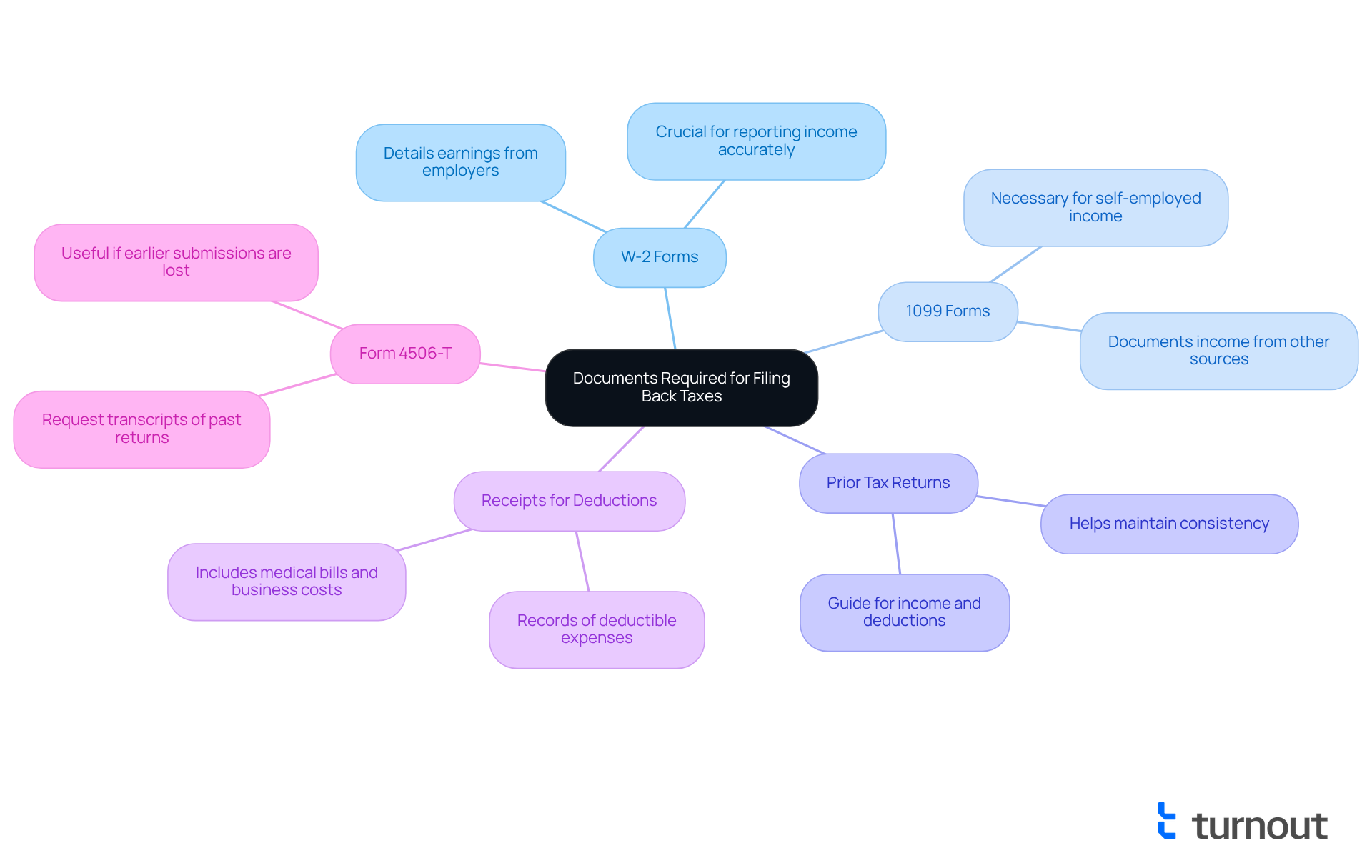
- W-2 Forms: These forms detail your earnings from employers and are crucial for reporting income accurately.
- 1099 Forms: If you are self-employed or received income from other sources, these forms are necessary to document that income.
- Prior Tax Returns: If accessible, these can act as a guide for your income and deductions, assisting in maintaining consistency in your submissions.
- Receipts for Deductions: Keep records of any deductible expenses, such as medical bills or business-related costs, as these can significantly impact your tax liability.
- Form 4506-T: This form allows you to request transcripts of your past tax returns from the IRS, which can be useful if you cannot find your earlier submissions.
It’s common to overlook crucial documents when submitting back taxes. Many taxpayers often miss W-2s and 1099s, leading to delays and complications. As tax expert Anthony Volodkin wisely states, "Being unquestionably proficient at organizing your documents is more crucial than any promotional endeavor; it establishes the groundwork for a successful submission."
With the IRS expecting over 140 million individual tax returns for the 2024 tax year, preparation is key. By collecting these documents in advance, you can simplify the submission process and enhance the accuracy of your tax return. This proactive approach can ease the complexities of knowing how many years can you file back taxes.
Additionally, with 275,948,000 visits to IRS.gov as of April 4, 2025, many individuals are seeking guidance on tax matters. This underscores the importance of being well-prepared. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—we're here to help you navigate through it.
Troubleshoot Common Issues When Filing Back Taxes
When filing back taxes, we understand that you may encounter several common issues:
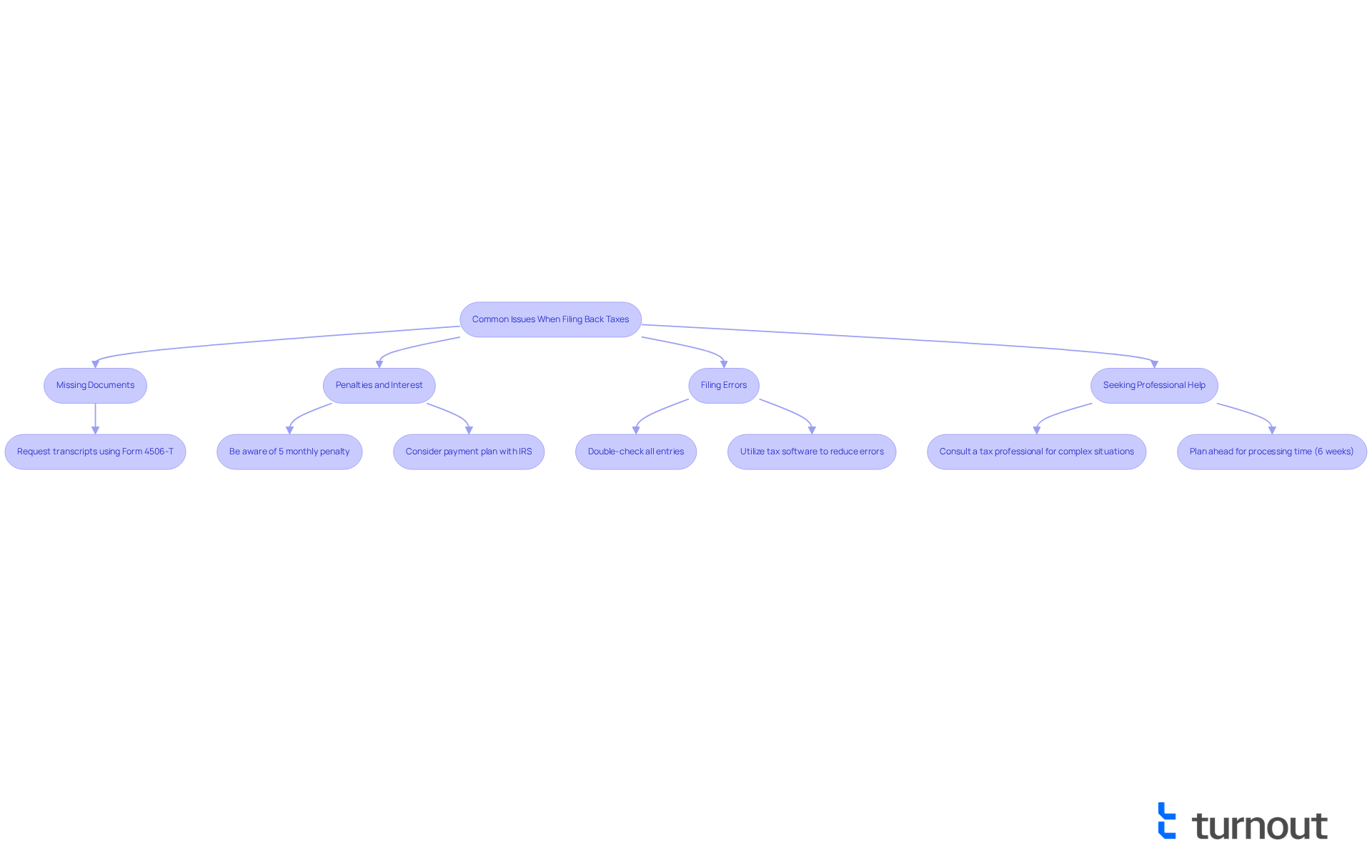
- Missing Documents: If you can’t find certain documents, don’t worry. You can use Form 4506-T to request transcripts from the IRS. This can help you reconstruct your income information effectively.
- Penalties and Interest: It’s important to be aware that filing late can lead to penalties. Individuals responsible for taxes often face a 5 percent monthly fee on unpaid amounts, which can accumulate rapidly. Additionally, there’s an extra 0.5 percent cost for late payments, capped at 25 percent. If you owe taxes, consider establishing a payment plan with the IRS to manage your debt more effectively.
If your tax situation is complicated—perhaps due to multiple years of unfiled returns or significant changes in income—it's wise to seek assistance from a tax professional to understand how many years can you file back taxes. They can provide tailored guidance to navigate your unique situation. Remember, it typically takes about 6 weeks to process an accurately completed past due tax return, so planning ahead is crucial. - Filing Errors: We encourage you to double-check all entries on your tax forms to avoid mistakes that could delay processing. Utilizing tax software can assist in reducing errors by guiding you through the submission process.
By being proactive and prepared, you can navigate these challenges effectively. Taxpayers with a good filing and payment history may qualify for penalty abatement, which can further alleviate financial burdens. As tax professional Annie Stephan emphasizes, "The IRS insists that taxpayers should act fast" to avoid escalating penalties. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Addressing back taxes is not just a matter of compliance; it’s a vital step towards achieving financial stability. We understand that navigating the complexities of tax regulations can feel overwhelming. However, by familiarizing yourself with the time limits and processes involved in filing back taxes, you can take meaningful control of your financial future.
Key insights from the article emphasize the importance of:
- Understanding IRS guidelines
- Gathering the necessary documentation for filing
- Filing back taxes within the stipulated timeframes to avoid penalties and potentially reclaim refunds
By being proactive and organized, you can effectively mitigate the risks associated with unpaid dues and fulfill your tax responsibilities with confidence.
Ultimately, addressing back taxes opens the door to improved financial opportunities and peace of mind. Taking action today not only helps you avoid severe consequences like wage garnishments or liens, but it also nurtures a healthier relationship with financial institutions. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Embracing this proactive approach can lead to a more secure and hopeful financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are back taxes?
Back taxes are amounts owed that remain unpaid after their deadline, often resulting from oversight, financial difficulty, or misunderstandings about payment responsibilities.
Why is it important to address back taxes?
Addressing back taxes is crucial to avoid significant penalties, accruing interest, and potential legal measures from revenue authorities, which can lead to severe consequences like wage garnishments, liens, and forfeiture of assets.
How many Americans are affected by unpaid dues?
In 2025, over 11.23 million Americans owed more than $125 billion in unpaid dues, highlighting the extensive nature of this issue.
What are the potential repercussions of not addressing overdue payments?
The repercussions can include wage garnishments, liens, and forfeiture of assets, as well as increased scrutiny from the IRS, especially for high-income non-filers.
How can unpaid dues affect individuals financially?
Unpaid dues can lead to financial instability for families and make it difficult for individuals to secure loans or mortgages due to their obligations.
What should individuals do if they have back taxes?
Individuals should swiftly address overdue payments to reduce repercussions and regain control over their economic futures, while also adhering to financial regulations.




